Root Canal Treatment

What is on this page
Overview. - .What is RCT?. - Why Root Canal Treatment?
Root Canal Treatment Cost - Root Canal vs Extraction - Root Canal Treatment Symptoms
Consequences of Delaying RCT - Root Canal Procedure - Root Canal Post Treatment Care
Root Canal Treatment Benefits. - Root Canal Side Effects - Root Canal Myths and Facts
OVERVIEW
OF
RCT
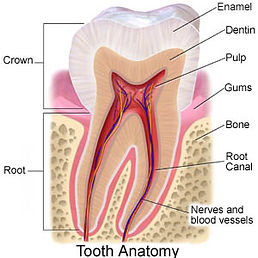
Understanding Tooth Structure and the Need for Root Canal Treatment
A tooth is made up of three main layers:
-
Enamel – The hard, protective outer layer
-
Dentin – The softer, yellowish layer beneath the enamel
-
Pulp – The innermost layer containing nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue
When Does a Tooth Need a Root Canal?
-
Enamel and Dentin Damage: If decay is confined to the enamel or dentin, it can usually be treated with a filling or restoration.
-
Pulp Infection: When the decay spreads deep into the pulp, it causes severe pain, inflammation, and infection. This is when a Root Canal Treatment (RCT) becomes necessary to remove the infected pulp, relieve pain, and save the natural tooth
Signs You Might Need a Root Canal:
-
Severe tooth pain while chewing or applying pressure
-
Prolonged sensitivity to hot or cold
-
Swollen, tender, or darkened gums
-
Pimples or abscesses on the gums
-
Cracked, chipped, or decayed tooth
WHAT
IS
RCT?
What is Root Canal Treatment (RCT)?
Root Canal Treatment (RCT), also known as Endodontic Therapy, is a specialized dental procedure designed to save a severely decayed or infected tooth. It targets the pulp — the soft, innermost part of the tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue.
When Do You Need a Root Canal?
-
Root Canal Treatment is necessary when the pulp becomes inflamed or infected due to:
-
Deep decay or cavities
-
Cracked or fractured teeth
-
Repeated dental procedures
-
Trauma to the tooth
Steps Involved in Root Canal Treatment:
-
Diagnosis and Examination:
-
Dental X-rays and clinical evaluation to assess the extent of infection.
-
-
Anesthesia and Isolation:
-
Local anesthesia to numb the tooth, followed by placement of a rubber dam to keep the area clean and dry.
-
-
Cleaning and Shaping:
-
Removal of infected pulp, followed by thorough cleaning, shaping, and disinfection of the root canals.
-
-
Filling and Sealing:
-
The cleaned canals are filled with a biocompatible material like gutta-percha and sealed to prevent future infections.
-
-
Restoration:
-
A dental crown or filling is placed to restore the tooth’s structure and function, providing long-term protection.
-
Why Choose Root Canal Treatment?
✅ Saves your natural tooth
✅ Prevents the spread of infection
✅ Restores normal chewing and biting function
✅ Prevents jawbone deterioration
✅ Improves overall oral health
What happens during a root canal treatment ?
When the caries, if left untreated, can penetrate deep into enamel and dentine and infiltrate pulp. This results in spread of infection in the root canal.
Spread of caries

Root canal treatment is designed to eliminate bacteria from the infected root canal, prevent reinfection of the tooth and save the natural tooth. When one undergoes a root canal, the inflamed or infected pulp is removed and the inside of the tooth is carefully cleaned and disinfected, then filled and sealed.

The first step in the root canal treatment is making an examination of the tooth so that the dentist understands the nature of the problem and is able to treat it effectively. This typically involves a physical examination of the inside of the mouth, in addition to X-ray imaging of the tooth to visualize the pulp chamber.
Next, a local anesthetic is administered to numb the tooth and increase the comfort of the patient during the procedure. A “dental dam” – a small protective sheet – is then put in place over the affected area to isolate the tooth and keep saliva and other substances away from it while the work is completed.
The dentist is then able to drill into the crown of the tooth to open it. This allows specialized dental instruments to be inserted into the pulp chamber and root canals to clean the inflamed or infected pulp from the area. The remaining space is then cleaned completely and shaped to make space for a filling, which will replace the pulp in the tooth.
The root canal can then be filled with a suitable biocompatible material, such as gutta-percha. Adhesive dental cement is also usually used to ensure that the root canal is properly sealed and to prevent future infections in the area.
Once the root canal has been filled, a temporary filling is usually put in place over the opening to seal it. Eventually, a crown is usually placed over the tooth to protect it over the long-term, but there is usually a waiting period between dental appointments while the crown is constructed. A temporary filling is useful during this time. At the subsequent dental appointment, the temporary filling can be removed and the tooth restored with a crown or other restoration.
How do you know if you need a root canal?
Root canals are needed for a cracked tooth from injury or genetics, a deep cavity, or issues from a previous filling. Patients generally need a root canal when they notice their teeth are sensitive, particularly to hot and cold sensations.
There are a few symptoms that mean you might need a root canal—
-
Severe pain while chewing or biting
-
Pimples on the gums
-
A chipped or cracked tooth
-
Lingering sensitivity to hot or cold, even after the sensation has been removed
-
Swollen or tender gums
-
Deep decay or darkening of the gums
Does a root canal treatment hurt?
Since patients are given aneasthesia, a root canal isn’t more painful than a regular dental procedure, such as a filling or getting a wisdom tooth removed. However, a root canal is generally a bit sore or numb after the procedure, and can even cause mild discomfort for a few days.
How much does a root canal treatment cost ?
The cost varies depending on how complex the problem is and which tooth is affected. Molars are more difficult to treat; the fee is usually more. Generally, endodontic treatment and restoration of the natural tooth are less expensive than the alternative of having the tooth extracted. An extracted tooth must be replaced with an implant or bridge to restore chewing function and prevent adjacent teeth from shifting. These procedures tend to cost more than endodontic treatment and appropriate restoration.